How does solar energy benefit your local community? Solar energy is much more than a tool for reducing personal utility bills. While homeowners and businesses celebrate lower energy costs, the true revolutionary power of solar lies in its profound ripple effects across the entire local community. This transition is not just about technology; it’s about building a more resilient, prosperous, and healthier neighborhood.
The critical question, How Does Solar Energy Benefit a community, is answered by looking closely at four key areas: economic empowerment, infrastructure resilience, public health, and social equity. This shift actively creates a robust foundation for a sustainable local future.
How Does Solar Energy Benefit Local Economies Through Job Creation
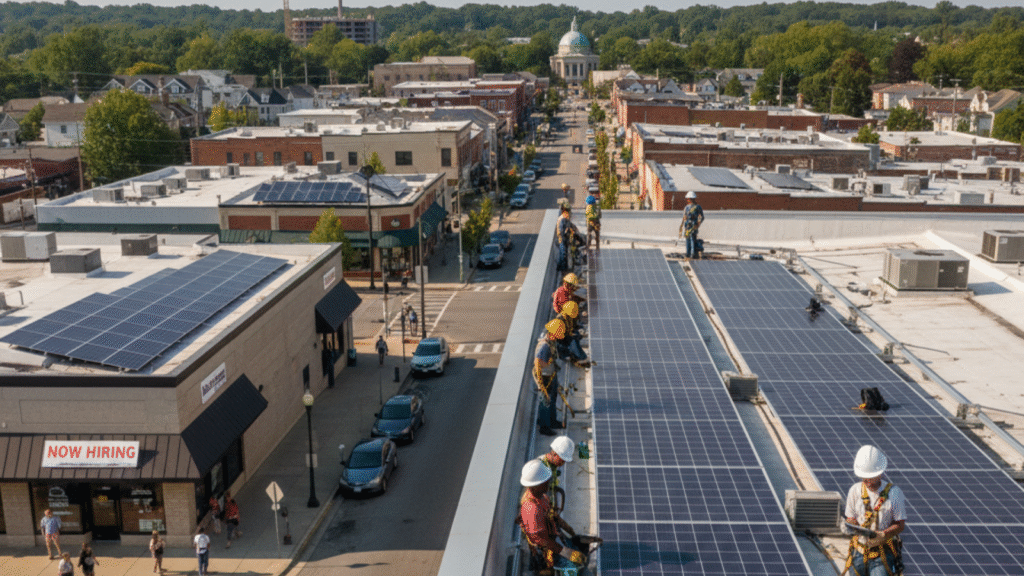

The solar industry has become a powerful engine for local economic growth, generating wealth and employment that stay within the community. This is perhaps the most immediate and tangible answer to how does solar energy benefit local workers and businesses.
Direct & Indirect Employment: Solar’s Job Creation Multiplier
Solar projects require a significant and continuous local workforce at every stage. Consequently, the economic impact extends far beyond the installation crew.
- Direct Job Creation: This sector actively requires a growing number of high-value, skilled positions. These include solar installers, certified electricians, skilled project managers, and sales consultants. Crucially, these are local jobs that cannot be outsourced, providing stable, competitive wages that increase local spending power.
- Indirect Economic Support: Furthermore, the demand for solar hardware, permits, and financing services supports local manufacturing, transportation, and financial institutions. Therefore, the capital invested in solar circulates multiple times within the community, using a positive multiplier effect that boosts the entire local economy.
Boosting Local Tax Revenue and Public Funding
For municipalities and local governments, widespread solar adoption creates a stable, new revenue stream that helps fund essential public services.
- Increased Property Tax Base: Large-scale solar farms and even commercial rooftop arrays often significantly increase the assessed property value of the land they occupy. As a result, this generates higher annual property taxes for the jurisdiction.
- Funding Public Services: This added revenue is often earmarked for vital public funds. In short, it helps pay for local school upgrades, road maintenance, and emergency services, benefiting every resident without necessarily increasing individual tax burdens.
| Key Economic Impact | Mechanism | Direct Local Benefit |
| Local Jobs | Installation, maintenance, and system design | Stable, high-skilled employment for local residents |
| Tax Revenue | Increased property taxes from solar infrastructure | Funding for schools and road maintenance |
| Economic Diversity | Attracts green technology investment | Reduces community reliance on a single, volatile industry |
How Does Solar Energy Benefit Grid Resilience and Reliability
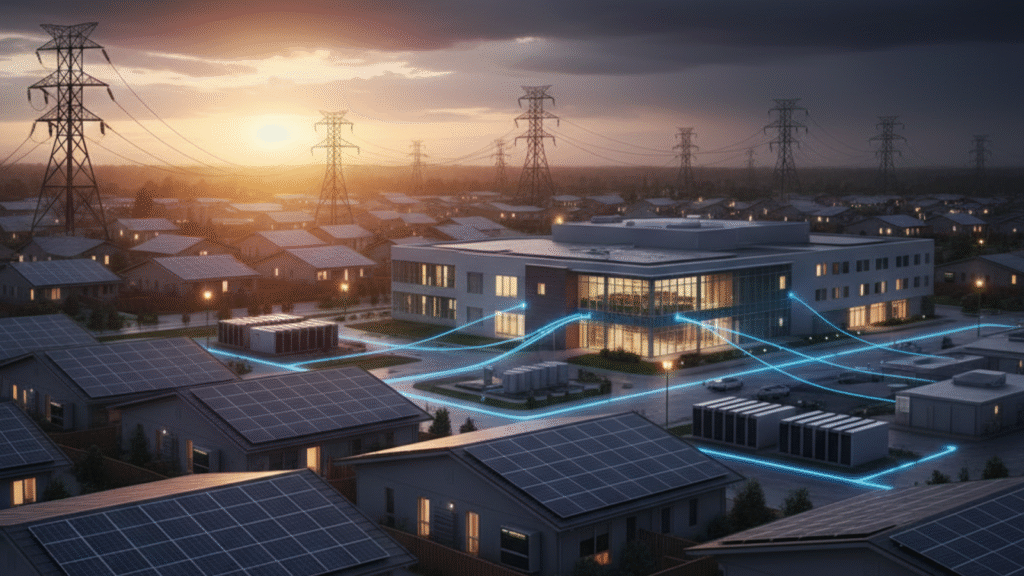

The centralized power grid is inherently fragile, vulnerable to single-point failures from natural disasters or technical issues. Solar power fundamentally shifts the equation by decentralizing power generation.
Decentralized Power for Disaster Preparedness
Indeed, solar power is a key component of modern disaster planning. Specifically, the distributed nature of solar makes the community highly resilient.
- System Resilience: Solar arrays installed on many homes and businesses create thousands of smaller, decentralized power sources. Thus, if a major power line goes down or a storm hits a substation, the power loss is contained, not widespread.
- Critical Microgrids: When coupled with battery storage (known as solar-plus-storage), a solar array can form an “islanded” microgrid. In this way, critical facilities—like hospitals, emergency shelters, and communication hubs—can actively disconnect from the main grid during a blackout and continue operating, ensuring public safety.
Reducing Grid Stress and Infrastructure Costs
Solar energy production naturally aligns with times of peak demand, providing crucial relief to the traditional grid.
- Peak Demand Shaving: Solar systems produce the most power midday, which often coincides with peak electricity demand (heavy use of air conditioning). Consequently, by providing power locally at this critical time, solar effectively reduces the demand peak on the utility’s centralized system.
- Lower Transmission Losses: Crucially, electricity transported over long distances loses energy (often 5-10%). When power is generated and consumed on-site via rooftop solar, those transmission losses are virtually eliminated. Therefore, solar minimizes energy waste and delays the need for expensive, publicly funded infrastructure upgrades.
How Does Solar Energy Benefit Public Health and the Environment
The shift away from burning fossil fuels to harnessing clean sunlight has a direct, measurable impact on the air people breathe and the water they consume. This is the community’s passive, long-term health dividend.
Clearing the Air with Zero Emissions
Traditional power generation releases vast amounts of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. Solar generation, conversely, is silent and clean.
- Zero Operating Emissions: Solar power generates electricity with zero harmful emissions at the point of use. This means every kilowatt-hour of solar energy actively displaces power that would have come from burning coal or gas, which release pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM).
- Improved Public Health Outcomes: A sustained reduction in these air pollutants directly correlates with fewer respiratory illnesses (like asthma), a lower incidence of cardiovascular disease, and reduced overall healthcare costs across the community. Ultimately, clean air makes a community healthier and more productive.
Conserving Water Resources
Additionally, solar power is an incredibly water-efficient energy source.
- Minimal Water Use: Unlike thermal power plants (coal, gas, nuclear) which require massive amounts of water for cooling and steam generation, solar photovoltaic (PV) systems use minimal to no water in their operation. Thus, this transition is vital for water-stressed regions, actively conserving precious local resources.
| Impact Area | Solar Energy | Traditional Power (Fossil Fuels) |
| Air Quality | Zero harmful emissions during operation | High CO2, SOx, NOx, and particulate matter |
| Noise Level | Completely silent operation | High noise pollution from plants and machinery |
| Water Usage | Minimal to none (only for cleaning) | High consumption for cooling and processing |
| Public Health | Reduced respiratory illness and community health costs | Increased respiratory and cardiovascular health risks |
How Does Solar Energy Benefit Social Equity and Education?
Beyond the financial and physical infrastructure, solar energy fosters a collective sense of purpose and provides tangible educational benefits.
Community Solar and Energy Equity
Not everyone can install solar—renters, apartment dwellers, or homes with shaded roofs face barriers. Fortunately, the community solar model solves this.
- Inclusive Access: Community Solar programs allow residents to subscribe to a shared local solar farm and receive credits on their utility bills at a guaranteed discount. Therefore, this model ensures that the economic and environmental benefits of solar are accessible to low- and middle-income households, promoting energy equity.
- Empowering Citizens: These programs actively empower residents to become “prosumers” (producers and consumers of energy), giving them a stake in the community’s energy future and shielding them from volatile utility rate increases.
STEM Education and Community Pride
Solar installations serve as visible teaching tools for future generations.
- Living Laboratories: When local schools or public buildings install solar systems, they become living laboratories for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education. Students can monitor energy production in real-time, integrating environmental stewardship directly into the curriculum.
- Fostering Stewardship: Ultimately, seeing their community invest in clean technology instills a sense of civic pride and encourages young people to pursue careers in the growing green energy sector.
Conclusion: Solar’s Lasting Community Dividend
The question, “How Does Solar Energy Benefit” a community, is answered with overwhelming evidence: it is a transformative investment in a sustainable local future.
In summary, by driving local job creation, ensuring stable tax revenue for public services, dramatically improving air quality to enhance public health, and decentralizing the power source to guarantee energy security during emergencies, solar power offers a holistic dividend. Choosing solar is not a passive choice; it is an active commitment to building a more resilient, economically vibrant, and healthier community for every single resident today and for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How Does Solar Energy Benefit a city’s ability to attract new businesses?
A: Businesses are increasingly attracted to areas with low, predictable operating costs and a commitment to sustainability. Crucially, solar energy provides both, giving the community a competitive edge by offering stable, low-cost power and a reputation as a leader in clean energy.
Q2: Does solar adoption reduce a community’s environmental footprint in manufacturing?
A: Indeed, while manufacturing solar panels requires energy, the operational lifespan of 25+ years ensures that a solar panel pays back its manufacturing energy debt—the time it takes to generate the energy used in its creation—in just 1-4 years. Therefore, for the rest of its life, it produces power with a net-zero impact.
Q3: How Does Solar Energy Benefit local governments through tax incentives?
A: Local governments often benefit from federal and state programs (like the U.S. Investment Tax Credit) designed to encourage solar adoption. These incentives attract outside capital for large projects, consequently increasing the local tax base without requiring local public investment.
Q4: Is solar truly a ‘green job’ creator, and are the jobs permanent?
A: Absolutely. The U.S. Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) confirms that these jobs are classified as Green Jobs. Furthermore, the jobs are highly permanent, spanning installation, specialized electrical work, and ongoing maintenance contracts, ensuring long-term local employment stability.

